Top 10 Types Of Heating Systems : Let’s Explore

You definitely have found yourself leveling up the thermostat to keep your house warm every time the outside temperatures drop. This is exactly what heating systems do. However, choosing the right type of heating system for your house will not only be efficient but will also be sustainable and save energy. In this article, we will be talking about the ten best types of heating systems that are best suites for your homes.
There is one core goal for every heating system, i.e., to transfer heat inside the living spaces to help maintain a comfortable and warm indoor environment.
While some homes have just one, many houses have more than just one heating system, particularly for the basements or additional rooms that require a different eating system than that of the entire house.
What Is A Heating System?
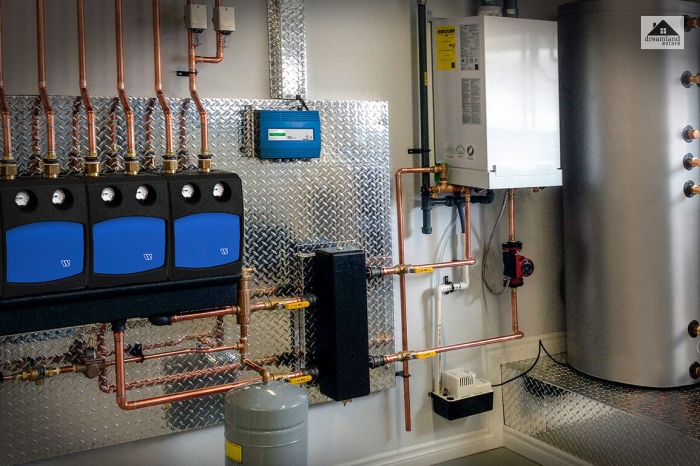

It is a heating mechanism that maintains temperatures at a preferable level by using thermal energy inside a home, office, or any other small space. It is a part of the HVAC [ heating, ventilation, air conditioning] system. Heating systems can be central or distributed depending on the space that it is heating.
Modern heating systems keep us comfortable during cold or chilly weather. Heating systems generate heat by converting a source of energy into heat or by using fuel.
Top 10 Heating Systems
Here are the ten different types of heating systems that provide a variety of ways to heat a house.
Furnace
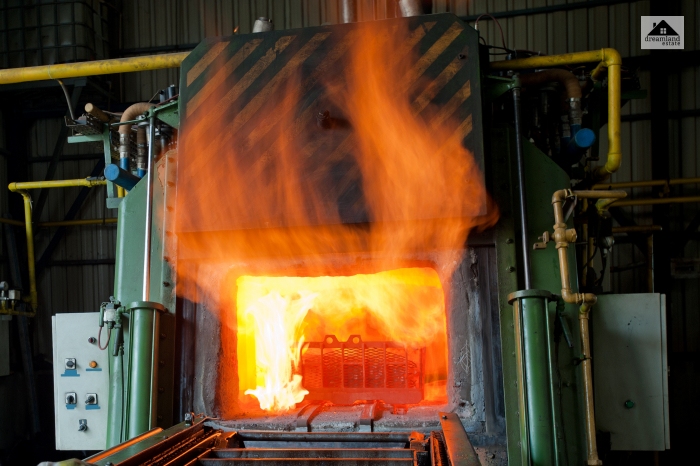

Forced air heating systems are one of the most preferable types of heating systems that are seen inside homes. This type of heating system uses a furnace with a blower fan that transfers the hot air to the various rooms in the house through a network of ducts.
Forced air systems use the same blowers and duct network as an air conditioner, therefore, are also good for cooling purposes during summers.
- Fuel Source: Gas, oil, propane, or electricity
- Advantage: Both cooling and heating systems are present in one system, hence, cost-effective.
- Disadvantage: Poses a threat of carbon monoxide poisoning, fire, or explosions.
Boiler
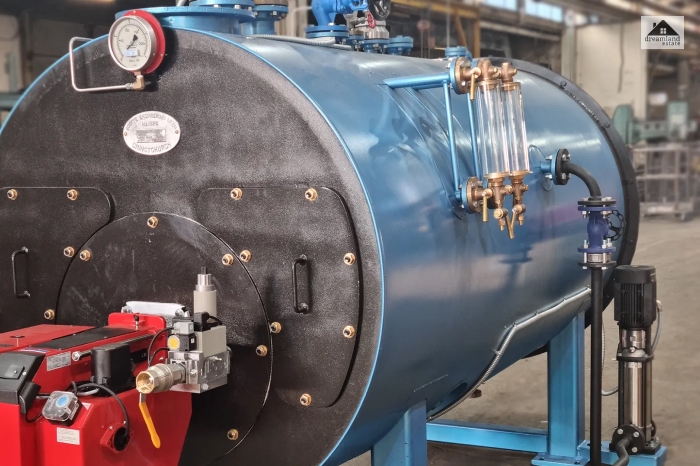

Traditional boiler or radiator systems are mostly present in old homes and apartments. They use a central boiler that circulates water or steam through pipes to the radiator units around the house.
Although it is very effective in heating or cooling secluded spaces, it is not a great choice for heating the more spacious areas inside a house all at once.
- Fuel source: electricity, biodiesel blends, propane, gas, and fuel.
- Advantage: does not dry out the air like other heating systems, hence provides comfortable heating.
- Disadvantage: they may not be in combination with an air conditioning system.
Heat Pump
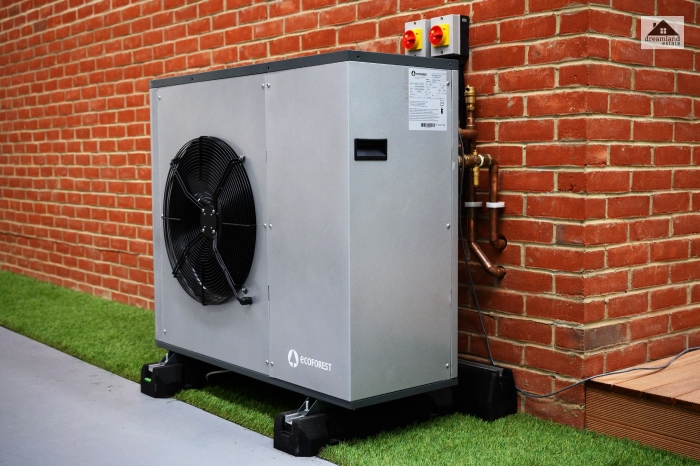

Heat pumps are the most recent type of heating system. They operate a lot like air conditioners. They extract the heat from the outside and transfer it inside the house through an indoor air handler. It is popular as a mini-duct or a ductless heating system.
- Fuel Source: Natural gas or electricity
- Advantage: It does not require ductwork, and one can be precisely control temperatures using wall units.
- Disadvantage: Does not work efficiently in frigid climates.
In-Floor Radiant
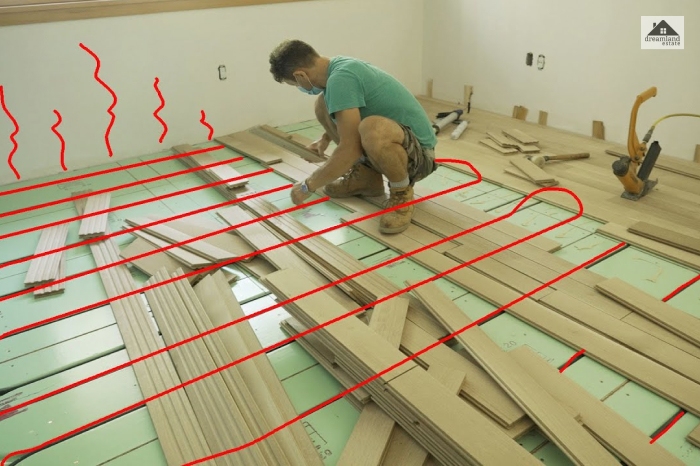

These systems distribute the heat throughout the house. They use plastic water tubing inside cement slab floors or are attached to the bottom of wooden floors.
They are not as noisy as the other types of heating systems but are slower in heating up or adjusting temperatures. But they are energy efficient and provide comfortable heating in every corner of the house.
- Fuel Source: Gas, electricity, propane, etc.
- Advantage: Provides steady, even, and comfortable heating across the whole house.
- Disadvantage: Hidden piping systems create major complications during maintenance.
Electric Resistance
Electric home heating is not the primary choice due to the high electricity costs. Although they are easy to install, they relatively get more expensive. They do not have any movable parts and hence do not require maintenance, ductwork, etc.
- Fuel Source: Electricity
- Advantage: They are versatile and you can install them in anyplace.
- Disadvantage: Runs on electricity, hence increasing electricity bills.
Baseboard Heater
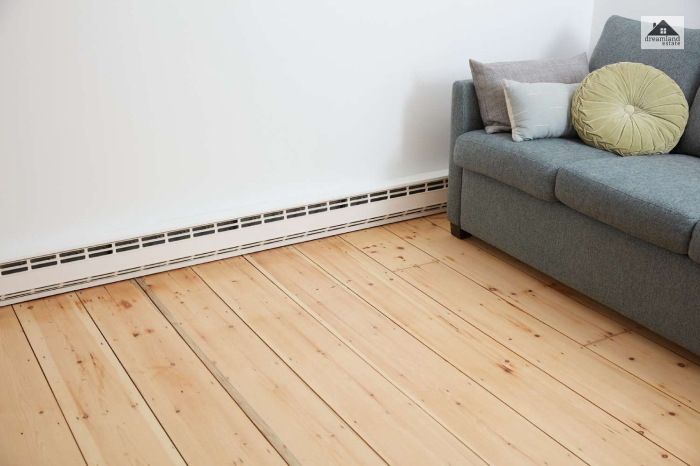

These are modern forms of highly efficient radiant heat and are also known as hydronic systems. The heated water from a central boiler circulates through a system of water pipes to baseboard heating units.
- Fuel Source: Electricity, gas, propane.
- Advantage: They offer an accurate temperature control mechanism.
- Disadvantage: Cannot be combined with an air conditioning system.
Electric Space Heater
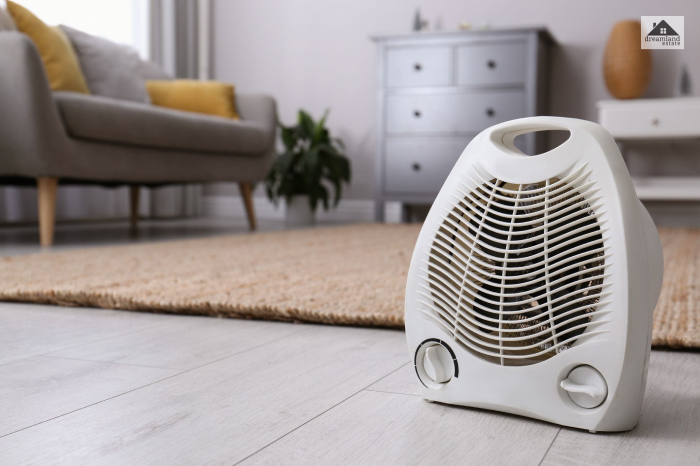

Also known as portable or plug-in heaters, they are an excellent temporary solution that provides targeted and controlled heat within the least time after being plugged into an electric source.
These are oil-filled and directly convert electricity into heat.
- Fuel Source: Electricity
- Advantage: Immediately heats after being plugged.
- Disadvantage: Not capable of heating a whole house or room.
Active Solar Heating
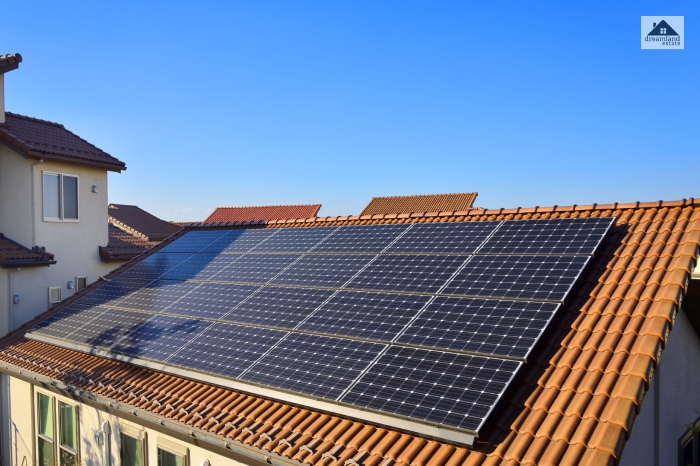

As the name suggests, it uses solar energy to heat a fluid which then transfers the solar heat directly inside the indoor space or is stored for future use.
Although, they cannot function all by themselves and rely on old heating systems to operate
effectively.
- Fuel Source: Solar energy
- Advantage: Sustainable and environment friendly
- Disadvantage: Cannot function 100% effectively without traditional heating systems.
Hybrid Heating
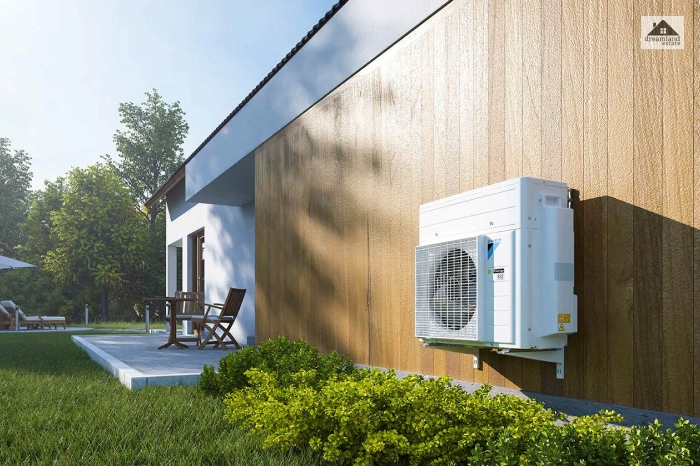

These types of heating systems merge the energy efficiency of a heat pump with the power of a gas furnace. The total functional capacity of a heat pump, when combined with the ability of a furnace to settle on a desired temperature during extreme weather, causes significantly less strain on the systems, along with efficient heating.
- Fuel Source: Electricity and natural gas.
- Advantage: Provides complete heating as it operates even in extreme weather.
- Disadvantage: Requires regular maintenance and yearly service checks.
Gravity Air Furnace
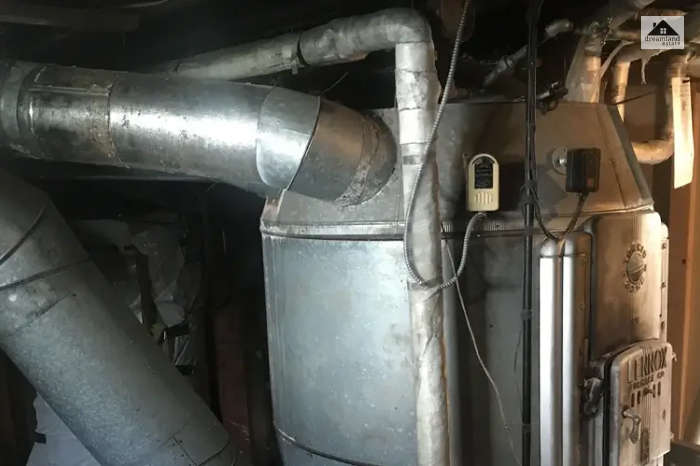

It is a modern take on the traditional furnace heating system and distributes heat through ducts. It doesn’t force the heated air through a blower but lets the war air rise while the cool air sinks down.
When the air is heated by a furnace in the basement, it rises inside the rooms through the doors, while the cold air passes down to the furnace through cold-air return ducts.
- Fuel Source: propane, gas, electricity
- Advantage: Due to the lack of moving parts, it does not require maintenance.
- Disadvantage: It takes a mentionable amount of time to adjust temperatures as the system functions on simple convection currents.
Bottom Line
The more you understand the different types of heating systems, the more you will be aware and well-read before making the best decision for your home or even deciding which heating system suits best for a homely accommodation.
Staying well aware of the best suitable options will help you to save not only time but also money down the road.
Read More:











Leave A Reply